Introduction
The rapid advancement of technology is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. Two sectors experiencing significant disruption are consumer goods and agriculture. With increasing investments in artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and biotechnology, businesses are optimizing production, enhancing sustainability, and improving customer experiences.
This article explores how tech investments are reshaping these industries, driving efficiency, reducing waste, and creating smarter supply chains.
1. The Role of Tech Investment in Consumer Goods
The consumer goods sector is undergoing a digital revolution, with companies leveraging technology to meet evolving customer demands. Key areas of transformation include:
A. Smart Manufacturing & Automation
-
AI and Robotics: Factories are adopting AI-driven automation to enhance production speed and precision. Robots handle repetitive tasks, reducing human error and labor costs.
-
3D Printing: Companies use 3D printing for rapid prototyping and customized product manufacturing, cutting down on waste and lead times.
B. Personalized Consumer Experiences
-
AI-Powered Recommendations: E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Alibaba use AI to analyze consumer behavior and suggest tailored products.
-
Augmented Reality (AR): Brands like IKEA and Sephora use AR to let customers virtually “try before they buy,” improving engagement and reducing returns.
C. Supply Chain Optimization
-
Blockchain for Transparency: Companies like Walmart use blockchain to track product origins, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing.
-
IoT for Inventory Management: Smart sensors monitor stock levels in real time, preventing overstocking or shortages.
D. Sustainability Through Tech
-
Eco-Friendly Packaging: Startups are developing biodegradable and smart packaging solutions to reduce plastic waste.
-
Energy-Efficient Production: AI optimizes energy use in factories, lowering carbon footprints.
2. Tech Investment Revolutionizing Agriculture
Agriculture, one of the oldest industries, is now at the forefront of tech innovation. Investments in agri-tech are addressing food security, climate change, and labor shortages.
A. Precision Farming
-
Drones & Satellite Imaging: Farmers use drones to monitor crop health, detect pests, and optimize irrigation, reducing water waste.
-
AI & Machine Learning: Predictive analytics help farmers forecast weather patterns and optimize planting schedules.
B. Vertical & Indoor Farming
-
Hydroponics & Aeroponics: Urban farms grow crops without soil, using 90% less water than traditional farming.
-
LED Smart Lighting: Energy-efficient LEDs mimic sunlight, enabling year-round crop production in controlled environments.
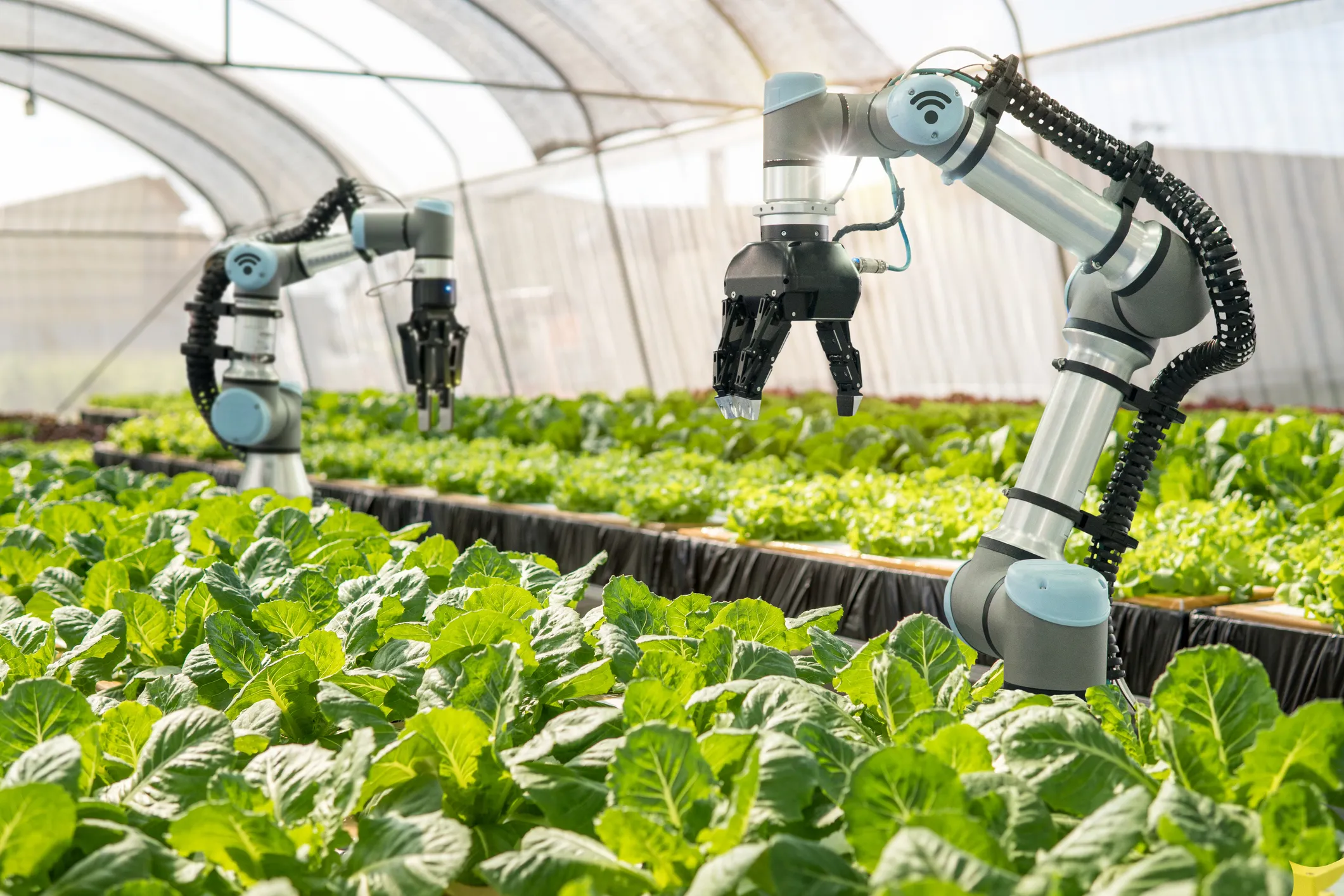
C. Robotics & Automation
-
Autonomous Tractors: Companies like John Deere are developing self-driving tractors that plow and harvest fields with minimal human intervention.
-
Harvesting Robots: AI-powered robots pick fruits and vegetables with precision, addressing labor shortages.
D. Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering
-
CRISPR & Gene Editing: Scientists are developing drought-resistant and high-yield crops to combat climate change.
-
Lab-Grown Meat: Startups like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods use biotech to create sustainable alternatives to traditional livestock farming.
E. Blockchain for Food Traceability
-
Consumers can scan QR codes to trace a product’s journey from farm to table, ensuring food safety and ethical sourcing.
3. Challenges & Future Outlook
While tech investments bring immense benefits, challenges remain:
A. High Initial Costs
-
Small farmers and businesses may struggle to afford advanced technologies without government or corporate subsidies.
B. Data Privacy & Security Risks
-
Increased connectivity raises concerns about cyber threats in IoT and blockchain systems.
C. Workforce Adaptation
-
Automation may displace jobs, requiring reskilling programs for workers.
Despite these hurdles, the future looks promising. By 2030, AI, IoT, and biotech are expected to:
-
Increase global food production by 70% to meet rising demand.
-
Reduce waste in consumer goods by 50% through smart logistics.
-
Cut carbon emissions via sustainable farming and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Tech investment is fundamentally reshaping consumer goods and agriculture, making them smarter, more efficient, and sustainable. From AI-driven supply chains to CRISPR-enhanced crops, innovation is solving age-old challenges while creating new opportunities.
As businesses and governments continue to invest in these technologies, collaboration will be key to ensuring equitable access and minimizing disruptions. The future of these industries lies in embracing digital transformation—ushering in an era of abundance, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
By staying ahead of tech trends, companies and farmers can not only survive but thrive in the rapidly evolving global economy.